Deploying Files using Artifacts
Artifacts in Thymis allow you to deploy files and directories to your managed devices. This is useful for distributing configuration files, scripts, certificates, or any other static files that your applications need.
Managing Artifacts
Artifacts are managed through the Artifacts tab in the Thymis sidebar:
- Navigate to Artifacts in the sidebar
- Click Create Artifact to add a new file
- Upload your file or enter content directly for text files
- Name your artifact and provide an optional description
Using Artifacts in Device Configurations
To deploy an artifact to your devices:
- In your device configuration, add the Core Device Configuration module
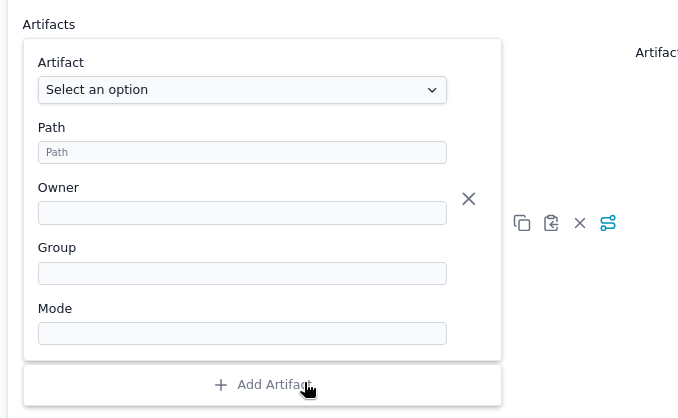
- Scroll to the Artifacts section
- Click Add Artifact
- Select the artifact you want to deploy
- Specify the destination path on the device
- Set permissions (owner, group, and file mode)
The artifact will be deployed to the specified path on all devices using this configuration.
Referencing Artifacts in Custom Modules
In your custom Nix modules, you can reference artifacts using the path:
"${inputs.self}/artifacts/<artifact-name>"This allows you to include artifact files in your Nix expressions:
systemd.services.my-service = {
script = "${inputs.self}/artifacts/my-script.sh";
# ...
};Best Practices
- Use descriptive names for artifacts to easily identify their purpose
- Organize related artifacts into directories using prefixes (e.g.,
configs/app.conf) - Set appropriate file permissions based on security requirements
- Keep artifact sizes reasonable for efficient deployment
Security Considerations
Artifacts are stored in plain text in the project repository. For sensitive files:
- Use Secrets instead of artifacts for passwords, API keys, or certificates
- Encrypt sensitive files before adding them as artifacts
- Restrict access to the project repository if it contains sensitive artifacts